
Understanding Insulin Testing: What You Need to Know
When it comes to metabolic health, insulin resistance plays a major role—but standard lab tests don’t always catch it early. Many people rely on glucose levels or A1c to assess their risk for metabolic dysfunction, but these markers only tell part of the story. Insulin resistance often develops long before blood sugar levels rise, making insulin testing and related metabolic markers crucial for early detection.
If you have PCOS or are concerned about insulin resistance, understanding which tests provide the most valuable insights can help you take control of your health.
Why Testing Insulin Matters
Insulin resistance is one of the main drivers of PCOS, weight gain, and metabolic disorders like Type 2 diabetes. While glucose tests and A1c measure blood sugar levels, insulin tests reveal how much insulin the body is producing to keep glucose in check.
For example, fasting glucose might appear normal for years while insulin levels are elevated. This is because the body compensates by overproducing insulin to keep glucose within range. By the time blood sugar levels rise, insulin resistance has often been present for a decade or longer.
Testing for insulin resistance early allows for intervention before more serious metabolic issues develop.
How to Measure Insulin Resistance
There are several ways to assess insulin resistance, including fasting insulin tests, but additional metabolic markers can provide even more insight.
- Fasting Insulin: Measures insulin levels after an overnight fast. High fasting insulin suggests insulin resistance, even if glucose is normal. Ideal fasting insulin levels are below 8 mIU/mL.
- HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance): Uses fasting insulin and fasting glucose to estimate insulin resistance. A HOMA-IR score below 1.7 is generally considered optimal, while higher values suggest insulin resistance.
- TG/HDL Ratio: This is an indirect measure of insulin resistance using triglycerides and HDL cholesterol. A high TG/HDL ratio is strongly associated with metabolic dysfunction.
- Lipid Panel: Elevated triglycerides and low HDL cholesterol are common in insulin resistance and indicate increased cardiovascular risk.
- CRP (C-Reactive Protein): A marker of inflammation that can indicate chronic low-grade inflammation, which is often linked to insulin resistance.
- A1c: While not a direct measure of insulin resistance, A1c reflects average blood sugar levels over the past few months. A higher A1c can indicate worsening metabolic health.
How Our Lilli Kits Can Help
Our Lilli Metabolic Testing Kits are designed to provide a comprehensive view of metabolic health by measuring multiple key markers associated with insulin resistance. Instead of focusing solely on glucose, our kits assess:
- Fasting insulin
- HOMA-IR
- TG/HDL ratio
- Full lipid panel
- CRP (inflammation marker)
- A1c
This allows for a more complete picture of metabolic function, helping to identify insulin resistance before it progresses to more serious conditions.
How to Get Your Insulin Tested
There are several ways to test for insulin resistance:
-
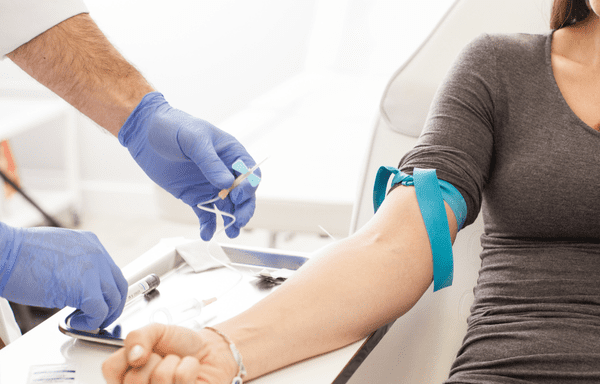
Through Your Healthcare Provider
- Pros: Your doctor may be able to provide guidance and help interpret results, but not always.
- Cons: Insurance may not always cover insulin testing, and some doctors may be unfamiliar with interpreting insulin resistance markers.
-
Quest Diagnostics or LabCorp
- Pros: Allows you to order the test directly without needing a referral.
- Cons: Costs can vary and may not be covered by insurance.
-
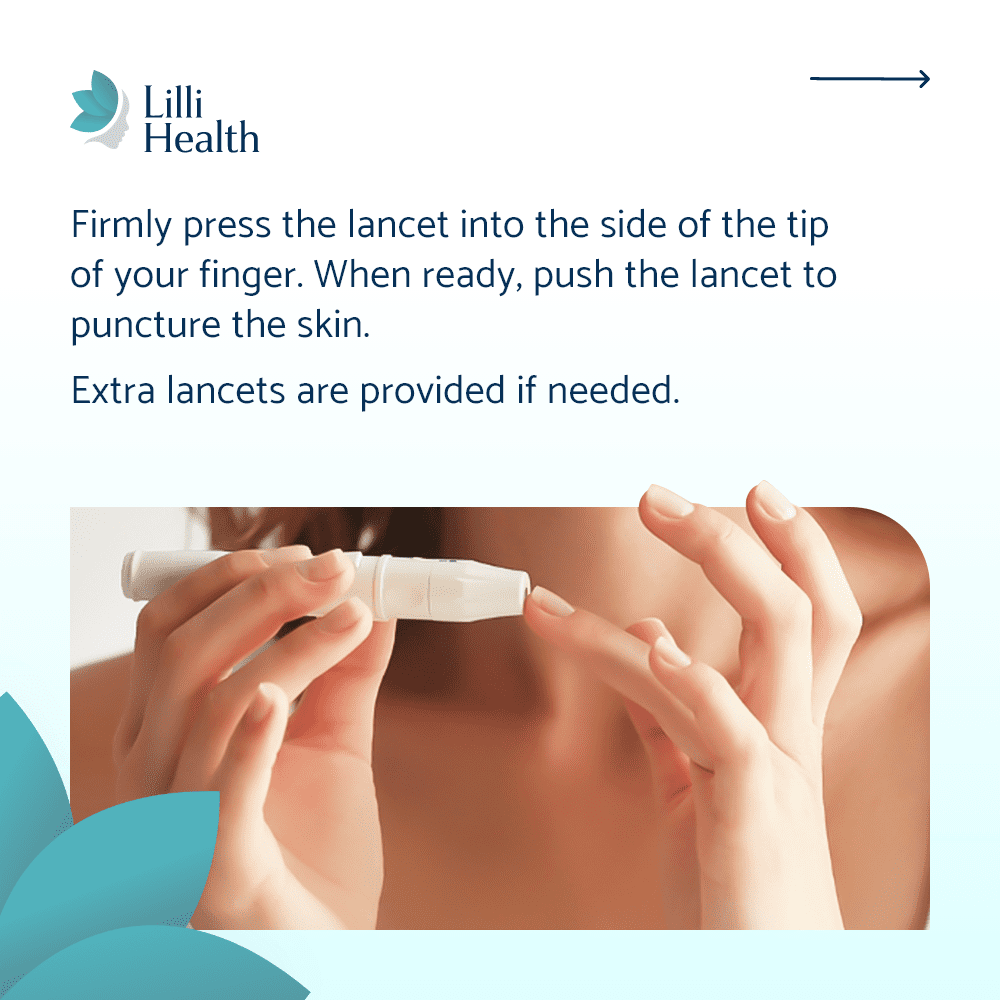
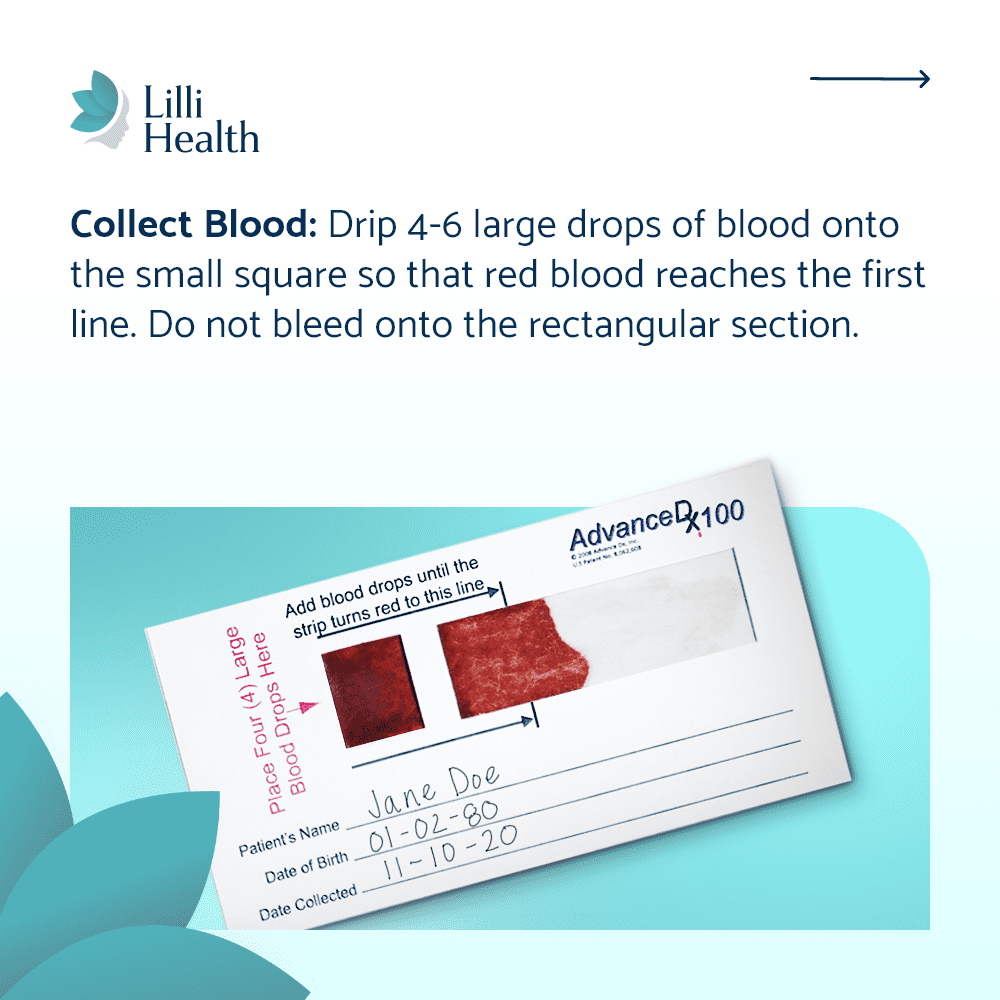
Lilli Metabolic Testing Kit
- Pros: Convenient and accessible, our kits provide a comprehensive look at insulin resistance markers without requiring a lab visit. HSA/FSA-approved.
- Cons: Not covered by insurance, but a more convenient alternative to standard lab testing. Automatically syncs with the Lilli App!
Understanding insulin resistance is a critical step in taking charge of your health, especially for those with PCOS or metabolic concerns. Measuring fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, lipid ratios, and inflammation markers can provide a much clearer picture than glucose alone.